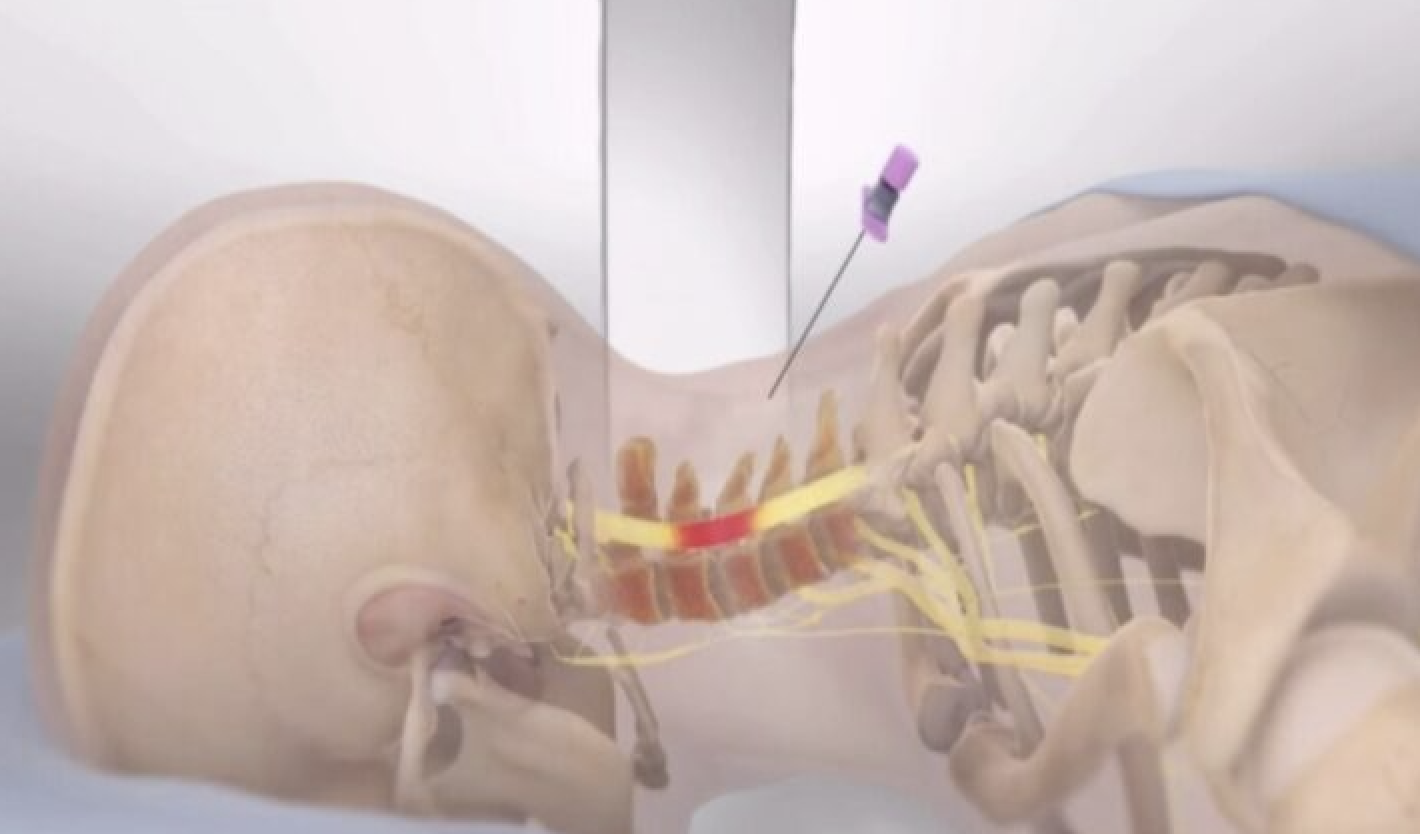
Epidural Steroid Injection
Introduction
This is a minor procedure performed to relieve pain in the cervical [neck], lumbar [low back] and associated radicular symptoms in the arms and legs, respectively. It can also be done in the sacral region as Caudal epidural, especially for patients that had lumbar fusion and persistent sacral pain, below the level of the hardware, with radicular symptoms.The pain is due to inflammation of the spinal nerves caused by disc herniation or spinal stenosis. Pain relief may last for couple of days or months and patients will be able to engage in physical therapy modalities to improve their level of functions.
 How is Epidural Steroid injection done?
How is Epidural Steroid injection done?
Depending on the location of the pain, the epidural steroid injection can be done in the Cervical, lumbar, or Caudal regions. A fluoroscopic machine is often used to locate the specific spinal level of the injection and to confirm that the medication is deposited in the actual epidural space.
The medications injected into the epidural space include a steroid such as Methylprednisolone and a local anesthetic such as Bupivacaine. A dye is often injected first to confirm needle location in the epidural space and not in a blood vessel.
For most patients, intravenous sedation is provided for some level of comfort and pain control especially for the immediate post-procedure period.
 Who will benefit from the procedure?
Who will benefit from the procedure?
Patients with pain in the cervical and lumbar regions, especially with associated radicular symptoms to the arms or legs respectively may benefit from the procedure. The specific spinal conditions include:
- Herniated disc: the disc material may rupture or bulge and cause irritation of the adjacent spinal nerves leading to swelling and pain.
- Degenerative disc: degenerative process can lead to collapse of the disc space, and growth of bone spurs and nerve root irritation.
- Spondylolisthesis: the vertebra can slip forward due to problems with the facets leading to compression of the nerve roots.
- Sciatica: compression of the 5th lumbar or first sacral nerves will result in pain along the Sciatic nerve with radiation to the buttocks and down the legs.
- Spinal Stenosis: this can lead to back pain and weakness and pain in the legs with walking.
Any risk associated with the procedure?
This is a relatively safe procedure. However, potential risks included:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Nerve injury
- Persistent pain
Preparation for the procedure
- You must let the office know all the medications you currently take.
- Continue all BP medication
- If you take insulin for diabetes, you may be asked to take half your usual morning does toprevent low blood sugar the day of procedure.
- Cardiac patients on certain heart medications may require clearance from their Cardiologist.
- All blood thinners such as Coumadin, Lovenox, Plavix, Eloquiz, and others must bediscontinued at least 2 days prior to procedure.
- Because you will get intravenous sedation, we advise you stop taking food and beverages 6hours before the procedure. Little sips of water can be taken with your medications.
- If you feel unwell the day of your procedure, please notify the office.
After the procedure
- Do not sign any document or drive machinery after the procedure because your judgment will still be impaired from sedatives.
- You must bring a responsible adult to accompany or drive you home.
- You will be provided with Discharge Home Instructions.
- The office will call you within 24 to 48 hours after your procedure, but feel free to call withany concern.
Radiofrequency ablation of the Knees [RFA]
Introduction
Osteoarthritis is a common medical condition that affects the knee joint. When advanced it leads to severe pain with associated difficulty in ambulation. When conservative measures fail, then knee replacement becomes imperative.
However, certain patients continue to experience intolerable pain after knee replacement. Some patients may not be fit for surgery due to other comorbid conditions or are right candidates for surgery but prefer nonsurgical means to alleviate the pain.
The knee is supplied by articular nerves called Genicular nerves located at specific locations of the knee. To determine patient that will be the right candidate for Radiofrequency ablation, a Genicular Nerve Block is done first.
Diagnostic Genicular Nerve Block of the Knee
This is a short procedure done using fluoroscope to identify the location of the nerves. Often mild sedation is needed because of pain when the periosteum of the bone is penetrated. Local anesthetics such as Bupivacaine or Lidocaine is used. Pain relief is assessed within 24 hours. A positive result is when pain is reduced by at least 50% for few hours. This is often repeated and if a positive response is determined then the patient advances to Radiofrequency ablation of the nerves for a longer duration of pain control.
 RFA of Knee
RFA of Knee
This is a minor procedure done to deaden the nerves that carry pain sensation from the Knee to the brain. A heated probe is used, and pain transmission is often halted for couple of months while preserving other functions of the nerve like sensation or muscle contraction.
A fluoroscope machine is used to identify the exact location of the nerves. Mild sedation is given prior to the procedure for some comfort to the patient. Patient is often required to verify that sensation produced before the “burning” of the nerve is the location of the pain. Pain may still be felt for couple of days after the procedure from the heat produced. Within 1 to 2 weeks the benefit, if any, should be produced and may last for couple of months. There may be a relapse in the pain afterwards because the nerves are known to regrow after few months.
Any risk associated with the procedure?
This is a relatively safe procedure. However, potential risks included:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Nerve injury
- Persistent pain
Preparation for the procedure
- You must let the office know all the medications you currently take.
- Continue all BP medication
- If you take insulin for diabetes, you may be asked to take half your usual morning does toprevent low blood sugar the day of procedure.
- Cardiac patients on certain heart medications may require clearance from their Cardiologist.
- All blood thinners such as Coumadin, Lovenox, Plavix, Eloquiz, and others must bediscontinued at least 2 days prior to procedure.
- Because you will get intravenous sedation, we advise you stop taking food and beverages 6hours before the procedure. Little sips of water can be taken with your medications.
- If you feel unwell the day of your procedure, please notify the office.
After the procedure
- Do not sign any document or drive machinery after the procedure because your judgment will still be impaired from sedatives.
- You must bring a responsible adult to accompany or drive you home.
- You will be provided with Discharge Home Instructions.
- The office will call you within 24 to 48 hours after your procedure, but feel free to call withany concern.
Trigger Points Injection [TPI]
This is a minor procedure done in an office setting to relieve pain in tender areas of muscles called trigger points. Trigger points are knots or nodules formed in muscles that fail to relax often due to chronic inflammation or spasms. This is often seen in the upper back muscles where the pain can be referred to the neck and shoulder when pressure is applied. It is also common in the low back area muscles.
The injection is often done with local anesthetics such as lidocaine or bupivacaine. Occasionally, it is combined with corticosteroids such as triamcinolone or methyl-prednisolone. This is highly effective and can be repeated in a couple of weeks if necessary. However, when steroids are added it is advised to limit the frequency because of potential of muscle breakdown.
Medical Conditions that can be treated with Trigger Points injection
- Chronic Neck and Low Back pain: chronic musculoskeletal pain conditions are often associated with muscle spasms which could lead to trigger points formation in different parts of the muscles.
- Fibromyalgia: this is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the muscles. There is often associated arthritic states such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, or lupus erythematosus.
- Chronic myofascial pain syndrome: this is also a chronic connective tissue disorder with inflamed muscle and tender spots that responds to TPI.
- Tension Headaches: the chronic stress results in tension in the muscles and development of knots and nodules in the muscles of the upper back and neck.
What happens after the injections?
Relief from the painful muscles is quick. However, there can be soreness from the needle puncture for couple of hours. Patient can apply ice or cold compresses at the areas.
When pain is relieved, it will be beneficial to continue massage of the muscles. Stretching and strengthening exercises can be optimized to break the pain-muscle spasms-pain cycle.
Is there any adverse effect from Trigger Points Injection [TPI]?
TPI is a relatively safe procedure. However, patient may have adverse effect from the local anesthetics or steroids, but this is very uncommon.
Bleeding and infection are very rare possibilities. To avoid muscle breakdown, steroid is used as infrequently as possible during a year period.
In general, trigger points injection is greatly beneficial in patients with chronic musculoskeletal conditions with associated trigger points and has rare adverse effects.
Steroid joint injection
Steroid injection into a joint is a minor procedure performed to provide pain relief of the joint caused by inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Injection can be completed in different joint including but not limited to the facet joints of the spine, sacroiliac joint, hip joint, shoulder, elbow, hand, Knee, ankle and foot. Injection of surrounding soft tissue may also be helpful for conditions such as tennis elbow.
How do I prepare for the injection?
Inform your doctor of all current medications. If you take blood thinner as they may need to be stopped a few days prior to the procedure. Sedation is not used for this procedure; however, you may choose to have family present to drive you home.
